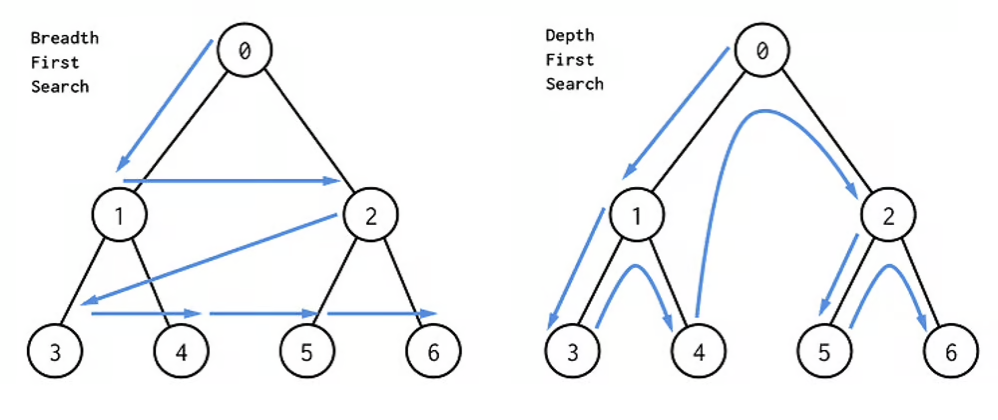
The general method/approach at which nodes are accessed can be of two types - Breadth First & Depth First
Methods under breadth first:
- Level order traversal (sometimes just referred to as bfs)
Methods under depth first:
- Pre-order
- In-order
- Post-order
Depth First traversal
We start from the root, keep building connections in a single direction then come back and complete other directions that were left incomplete.
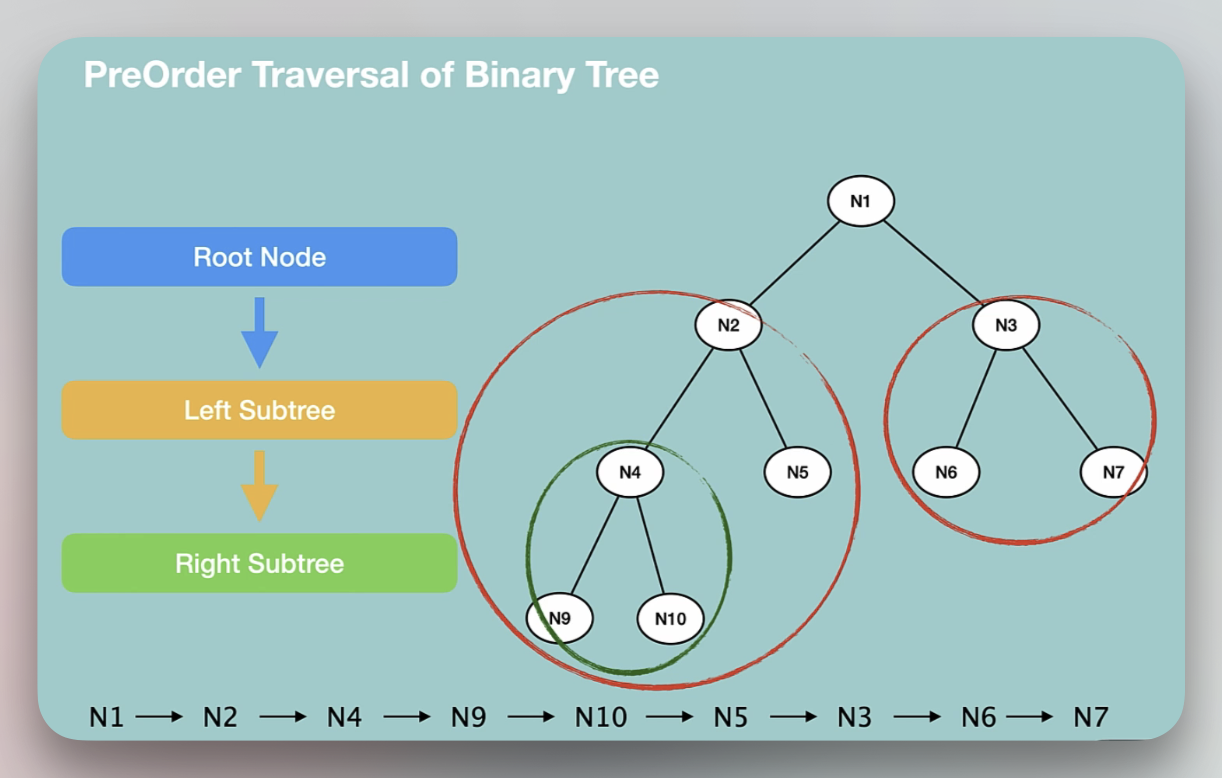
Pre-order traversal
Pre refers to the fact that the root node is visited before its children. Pre-order traversal visits nodes in the following order-
- Root node
- Left subtree
- Right subtree
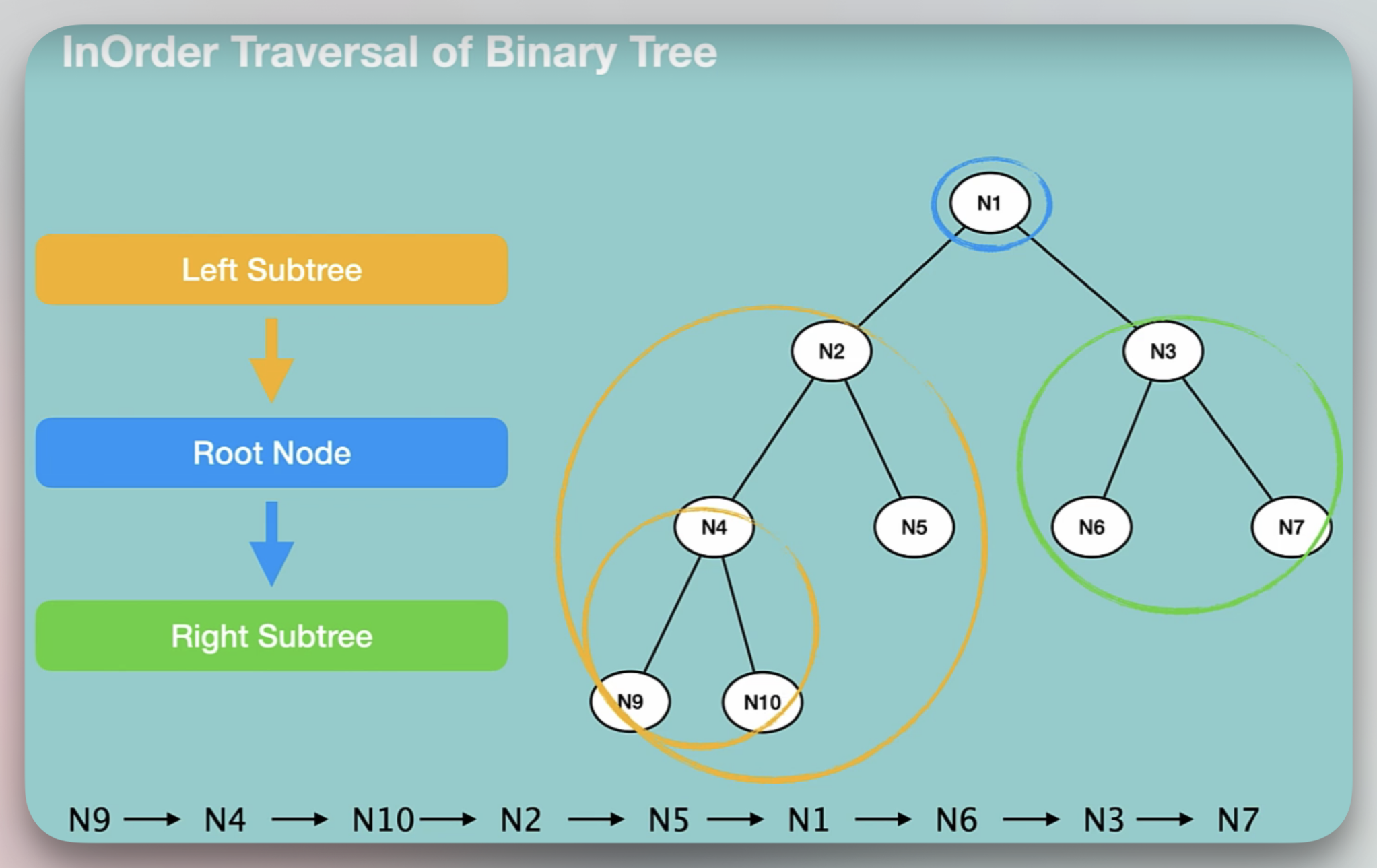
In-order traversal
In refers to the fact that the root node is visited in between its children. In-order traversal visits nodes in the following order-
- Left subtree
- Root node
- Right subtree
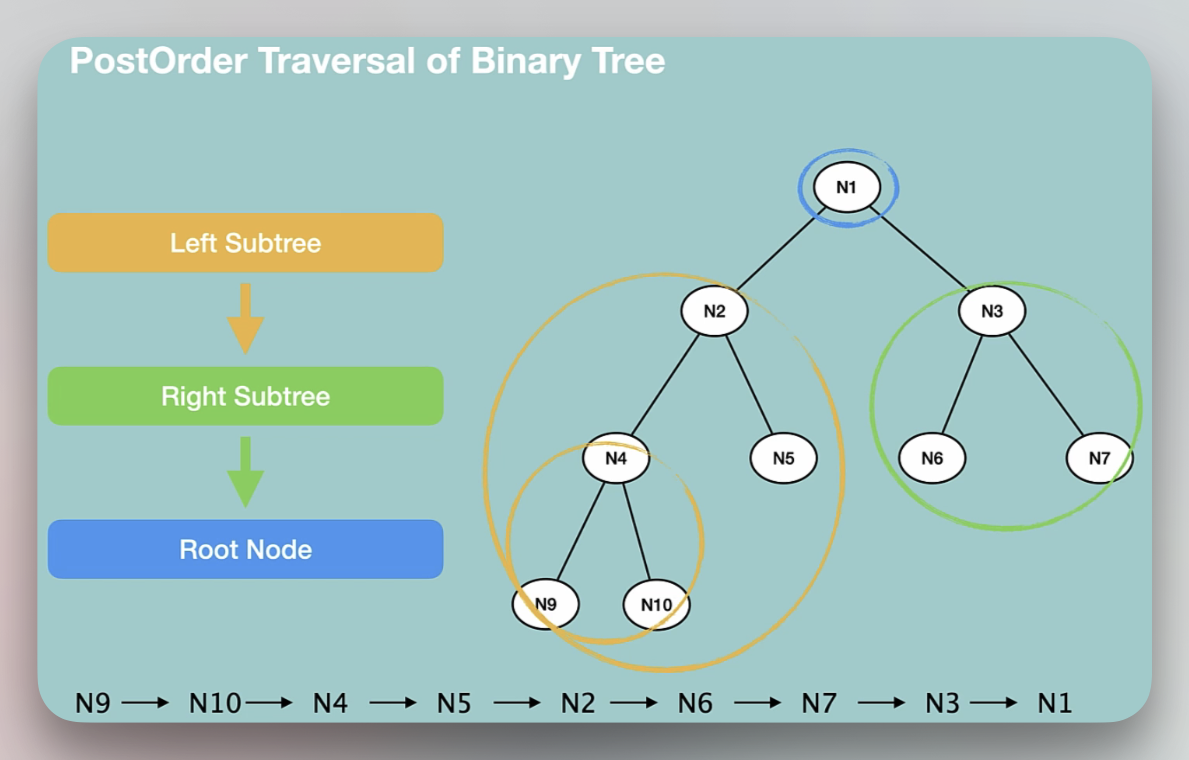
Post-order Traversal:
Post refers to the fact that the root node is visited after its children.
- Left subtree
- Right subtree
- Root node
Breadth First traversal
We start from the root, build connections uniformly in both directions and proceed downwards. This means each level is completed in order.
Level-order traversal
Level order traversal, also known as breadth-first search (BFS), is a tree traversal algorithm that visits all nodes at a given level (same distance from the root) before moving to the next level. Next level starts from the left every time.
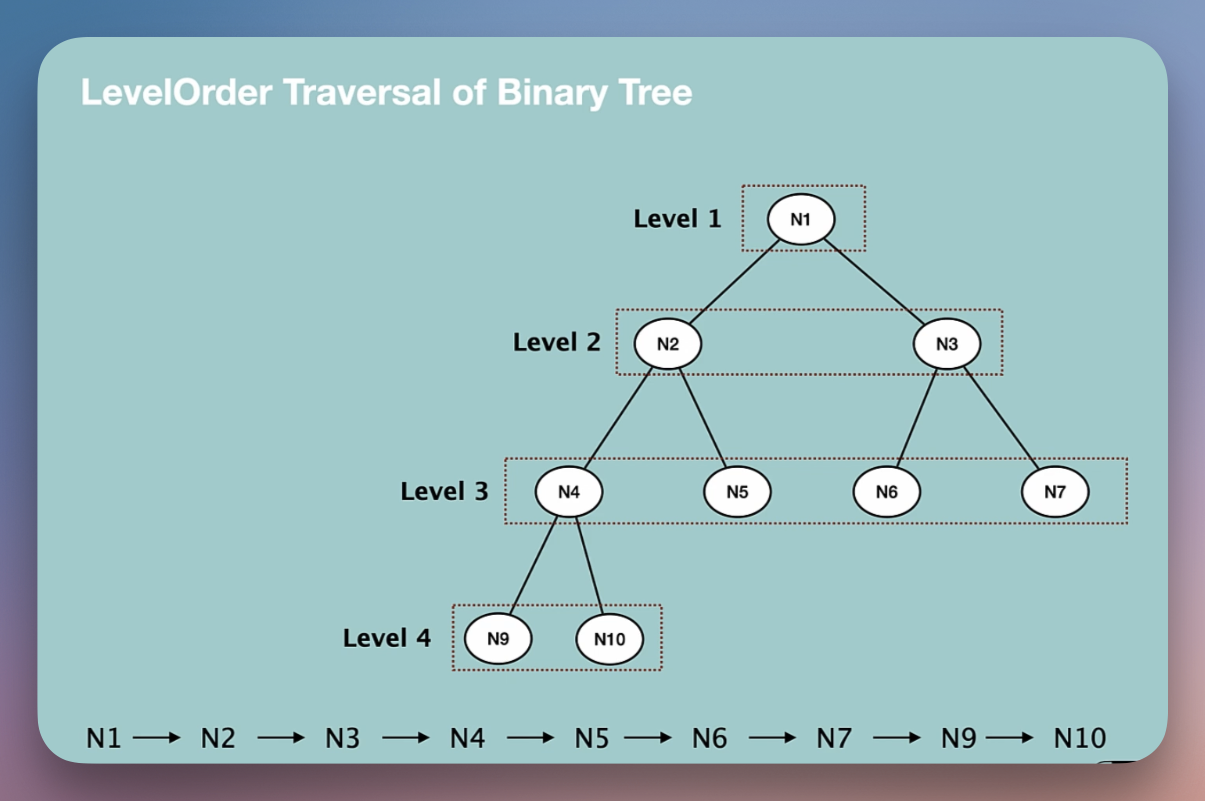
It is important to note that to implement BFS/level order, we require Queue data structure. The main reason for it is the FIFO principle in queue which is required for such traversal. How is this achieved using a queue? In the following way -
Maintaining Level Order:
- The queue acts as a temporary holder for nodes at the current level.
- Nodes are enqueued (added) level by level during the traversal.
- When processing a node, its child nodes are enqueued for exploration in the next level.
The FIFO relates to BF in such manner-
FIFO Principle Ensures Level Visit:
- The queue follows the FIFO principle, where the first element added is the first one removed (dequeue).
- This ensures that all nodes at the current level (enqueued earlier) are processed before moving on to the next level’s nodes (enqueued later).